Every vehicle requires an engine & fuel for its moving. The fuel helps propel the internal combustion engine & thus motion. There are different types of engines & fuels available for automobiles & two-wheelers, as well i.e, diesel & petrol engines. Here, a diesel and petrol (gasoline) fuel differs from a vehicle’s engine fluid called mobile. While both are needed for driving many cars, motorcycles, motorboats, aircraft, and several heavy-duty types of machinery, etc. These types of fuel also have their pros and cons, as well. So, let’s find out the difference between diesel vs petrol engines and which one can last longer.

In this blog, we are going to take an in-depth look at the comparison between diesel and petrol engines for their endurance and longevity.
What is Diesel Engines?
A diA diesel engine is a specific automobile motor that runs on diesel fuel. This fuel is available in an unrefined form also called crude oil. By using this fuel, fuel ignition takes place without a spark which results in compression of inlet air & then injection of fuel.


Diesel contains the naphthenes in a form of alkanes, a chain of 12 or more carbon atoms. Alkanes are the cleanest class of hydrocarbons for emission. These naphthenes consist highest energy density of all hydrocarbons. This diesel becomes the cleanest fossil fuel due to hydrocarbons emissions. Besides this, based on their chemical characteristics, diesel can have more energy thus, giving diesel engines a better fuel economy. The viscosity of diesel can increase in low temperatures, especially in frigid weather.
A diesel engine usually contains a four-stroke cycle. This four-stroke cycle defines as the four cycles that the engine needs to complete–intake, compression, combustion, and finally exhausted.
If we talk about carbon emission, diesel fuel will produce less carbon-based gases, such as carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. However, diesel is likely to produce suspended particulate matter that is not visible to our naked eye.
What are Petrol (or Gasoline or Gas) Engines?
Petrol engines are natural combustion engines that run on gasoline fuel. It is also known as a gasoline engine. This engine requires a spark through the spark plug for the air-fuel mixture ignition. These engines particularly available in the Americas includes regions in Latin America. Petrol is a fossil fuel that formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms such as plants, algae & bacteria.


Petrol is prepared through a mixture of alkanes and cycloalkane that contain a chain of hydrocarbons ranging from 5 and up to 12 carbon atoms. This means petrol usually has a shorter chain of hydrocarbons when compared with diesel. This type of fuel is less dense, has less energy, and does not have a very good fuel economy. It is also seen that, at low temperatures, the viscosity of petrol does not change significantly, given the weather. A petrol engine is like a diesel engine, which also contains a four-stroke cycle, i.e., intake, compression, combustion, and exhaust.
Aside from this, in terms of carbon emission, petrol seems to emit more carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide than diesel. However, petrol is not likely to produce suspended particulate matter.
Why do diesel engines last longer than petrol engines?
Now, to find out which auto-mobile engine type has more endurance and longevity, in terms of fuel efficiency. But first, we will need to understand how these engines function.


How Diesel and Petrol Engines Work
The petrol & diesel engines work as four-stroke engines. This four-stroke engine is a common type of internal combustion engine. It delivers one power stroke for every four piston strokes. These engines complex a certain cycle such as intake, compression, combustion & exhaust.
Firstly the vehicle engine’s piston moves & then starts from the downward position. It makes the intake valve open & the fuel & air mixed, then enter the cylinder. This process is called intake stroke.
Secondly, the piston then makes an upward movement, which causes the mixture of fuel and air to become compressed. Thus, because this cycle occurs, the process is also called the compression stroke. In the third stage, the process of what is called combustion in the cycle takes place. In this step, there may be a slight difference in the internal combustion system between a diesel engine and a petrol engine.
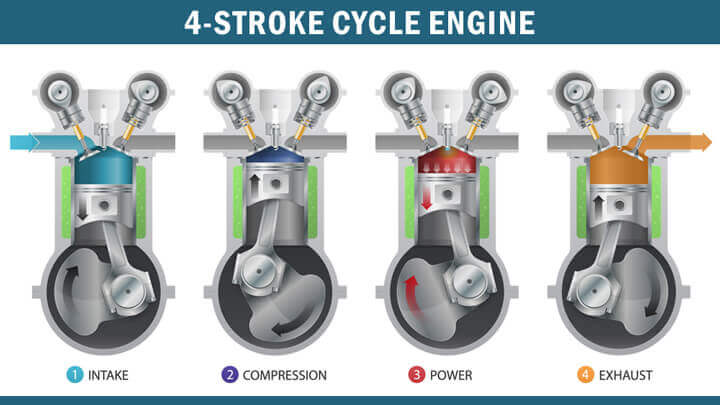

Finally, in the last stage, the exhaust valve opens, and the piston moves back in the upward direction. This cycle forces to let out the exhaust gases (carbon-based gases) from the exhaust valve and into the exhaust pipe located at the bottom rear of a car.
Now, if we talk about petrol engines, since their petrol fuel evaporates quickly, therefore, the fuel can be mixed easily with air. The one thing that is needed to ignite this fuel and air mixture is just a spark. Thus, that spark is generated through a spark plug connected via a wire. The spark plug can produce a spark and through it, it can quickly generate the stroke in the combustion cycle. On the other hand, a diesel engine cannot mix diesel fuel with air that well. Therefore, because of this, the diesel fuel is made to be compressed and atomized to achieve the function. It is then sprayed into the air, which has a higher temperature so that it can produce the combustion that is required.
Because of this, a major difference between the two fuel-run engines is that while a petrol (gasoline) engine requires a spark plug, a diesel engine rather needs a fuel injector to function. Next, there is the compression ratio between the two engine types. A diesel engine can run on a higher compression ratio since it only has to compress the air, whereas a petrol engine is required to compress a mixture of both petrol and air. This is also one of the main reasons why a diesel engine returns better fuel efficiency than a petrol engine.
Which is the more reliable diesel or petrol engine?
Diesel engines are significantly used in different types of vehicles such as commercial pickup trucks, SUVs, AWD cars & trucks. These diesel engines offer great mileage that delivers 25 to 30% better fuel economy. These engines generate more torque that helps the heavy-duty vehicles to carry various kinds of stuff for a longer duration. Here, torque is referred to as the moving force that is generated by the vehicle’s engine.
Thus, the main reason why a diesel engine can last much longer than a petrol engine is that diesel burns well in the engine. Even it helps in lubricating the essential parts of the internal combustion engine. It helps in the smooth functioning of engine components that make them more last longer. When compared to a petrol engine, petrol fuel is quite like a detergent that tends to quickly wash the oil away from the engine’s essential components. This may also result in quickly making the engine dry. Therefore, this is also the main reason why most components of a petrol engine wear out quickly.
This is also a reason that explains why the typical life span of a petrol engine is usually around 3,00,000 kilometers (or 186,411.35 miles) before the engine wears out.
However, the life span that of a diesel engine could easily last after being given around 5,00,000 kilometers (310,685.60 miles). Thus, many auto-mobile experts say that if maintained, properly, a diesel engine would even last for around 30 years, which is not quite possible for a petrol (gasoline) engine.
Conclusion
From this, we can conclude that diesel engines are better than petrol engines. These engines can last longer in fuel efficiency & longevity. But this diesel motor is more expensive than petrol in many countries. That’s why most car manufacturers use petrol engines in their vehicles rather than petrol engines.


Write A Comment